Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Used by ‘Majority’ of NCAA ATCs
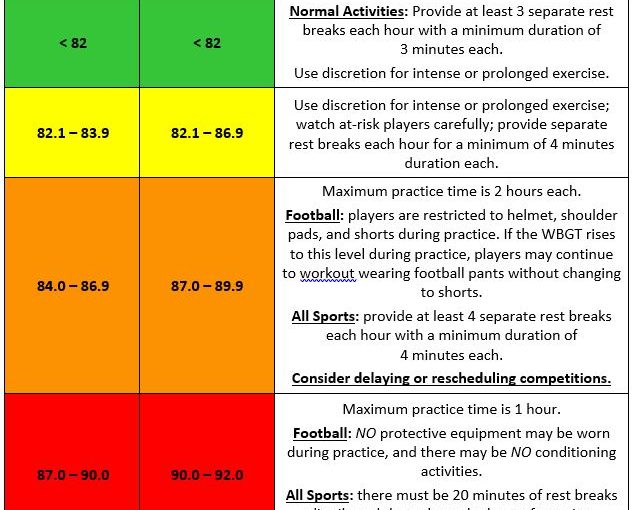
Heat illnesses present a major risk for athletes, especially football players. The National Athletic Trainers Association (NATA) established recommendations to prevent heat illnesses that include measuring wet bulb globe temperature (WBGT), but adherence to this recommendation is unknown.The WBGT is a comprehensive index that takes into account air temperature, humidity, and radiation. Specifically, WBGT includes the measurement of wet-bulb temperature (humidity), dry-bulb temperature (ambient temperature), and globe temperature (radiant heat). The WBGT value is used to assess the potential impact of environmental heat stress and establish exercise guidelines.
 NCAA sports other than football also use WBGT index to assess heat stress. Two sets of heat stress guidelines, each based on WBGT, were designed for men’s NCAA Championship Division I distance-running competitions, for instance. One set of guidelines was established to minimize the chance of heat injury during distance running events. A second set was designed to predict heat stress-related performance decrements
NCAA sports other than football also use WBGT index to assess heat stress. Two sets of heat stress guidelines, each based on WBGT, were designed for men’s NCAA Championship Division I distance-running competitions, for instance. One set of guidelines was established to minimize the chance of heat injury during distance running events. A second set was designed to predict heat stress-related performance decrements
A survey was sent to all 130 Division 1 FBS athletic training staffs to determine their use of the WBGT to assess heat stress. The results were collected and analyzed by the Utah State University professors before being published in May 2019 entitled, “Use of the Wet Bulb Globe Temperatures in NCAA FBS Athletic Training Staffs.”
Of the 82 respondents (63% response rate), 59 use WBGT to assess heat stress. However, only 19 use it for summer conditioning. Of the 23 universities that do not use WBGT, 10 noted that extreme heat or humidity is not an issue where they are located.
The majority of FBS training programs (72% of respondents) use the WBGT, but adherence to this NATA recommendation varies throughout the season (summer conditioning versus practice) and is likely influenced by the geographical location of the university.
To read the full study from Utah State University on the use of WBGT, click here.







